Understand 5G Wireless Technology
5G, stands for the fifth generation of cellular standards, is the most advanced form of mobile networking in present. 5G in smartphone are designed to tackle complexities of the hyper connected world and previous generations were just designed mainly to improve connectivity by call quality and boost data speeds.
With ultra-fast data speeds, near-zero latency, and the ability to connect millions of devices simultaneously, 5G isn’t just about better streaming or smoother video calls—it’s the backbone for innovations such as:
- Autonomous vehicles navigating in real time
- Smart cities powered by intelligent sensors
- Immersive AR and VR experiences
- Industrial automation in factories and logistics hubs
- IoT (Internet of Things) at massive scale
In short, 5G is the first mobile standard designed not only for people, but also for machines, industries, and cities.
A Brief History: The Road to 5G
- 2019: The first commercial 5G networks went live in South Korea, the U.S., and China.
- 2020–2022: In this era 5G are widely expand into major cities across Europe, Asia, and North America.
- 2023–2025: In todays, period 5G is widely adopted in suburban and rural areas, with manufacturing, healthcare and education sector which unlocks the new beginning in these sectors.
By the help of adoption of 5G nowadays emerging economies are quickly catching up.
The Role of Cellular Standards
To understand 5G, it helps to know about cellular standards—the rulebooks that dictate how mobile networks function. These standards are developed by global organizations like the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
They ensure:
Technical guidelines for building networks and devices.
Interoperability across different brands and countries.
Smooth evolution from one generation to the next.
For context, here’s how past standards shaped our world:
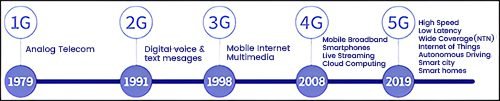
How Does 5G Work?
5G delivers excellent performance due to cutting-edge technology:
High-Frequency Spectrum (mmWave):
Uses millimeter waves between 30–300 GHz for ultra-fast speeds.
Gives a shorter range than 4G, as it requires more cell sites.
Small Cells:
Compact base stations placed on street poles, rooftops, and public areas.
Improve coverage in dense urban environments and cut down latency.
Massive MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output):
Handles thousands of connections at once due to dozens of antennas on a single tower.
Beamforming:
Provides faster and more reliable connections by directing signals to specific users.
Benefits of 5G
The shift from 4G to 5G unlocks a wide range of advantages:
100 Times Faster Speed: Up to 10 Gbps, compared to 4G.
Ultra-Low Latency: Less than 1 millisecond, critical for remote surgeries, gaming, and autonomous systems.
Massive Device Capacity: Can support up to 1 million devices per square kilometer.
Power Efficient: Helps devices transmit faster while conserving power.
Industry Innovation:
In Healthcare: Remote diagnostics, robotic surgeries.
In Education: Virtual classrooms and immersive training.
In Transport: Smart traffic lights, connected cars.
5G allows the use of apps with seamless VR, AR, and AI-powered experiences.
5G vs. 4G: A Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | 4G Network | 5G Network |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Up to 100 Mbps | Up to 10 Gbps |
| Latency | 30–50 ms | Under 1 ms |
| Device Load | Tens of thousands | Millions |
| Use Cases | Streaming, browsing | IoT, AI, automation |
5G for Home Internet
One of the most practical uses of 5G today is home broadband. By utilizing fixed wireless access (FWA), telecom providers eliminate the need for costly fiber cables:
A nearby small cell tower beams 5G signals to a receiver/router at home.
The router then distributes Wi-Fi indoors, just like traditional broadband.
This is especially game-changing for rural and underserved areas where wired internet is limited.
Impact of 5G on Mobile App Development
The app industry is already feeling the impact of 5G as the developers gets free-hand to create richer, smarter, and more responsive apps thanks to:
- IoT integration: Apps that seamlessly manage connected devices.
- Immersive tech: That gives smooth AR/VR and 3D experiences.
- Streaming: 4K/8K video and lag-free live broadcasting.
- Navigation: Help to navigate easily as it give ultra-precise GPS with real-time updates.
- Cloud-powered apps: Give a relief of taking heavy laptop everywhere, thanks to these lightweight apps that rely on cloud storage and computing.
- Advanced chatbots & tactile internet: Real-time interactions with haptic feedback.
Challenges of 5G Deployment
Despite of having lots of benefits in every sector, still 5G isn’t without hurdles:
- Its infrastructure is costly because it requires far more antennas and towers than 4G.
- Government have spectrum Management to allocate and regulate frequency bands.
- More prone to attacks because of larger network of devices.
- Rural and developing regions may experience slower rollout.
FAQs About 5G
Q1: How is 5G different from 4G?
Q2: Will my 5G phone still work on 4G?
Q3: Is 5G the same as Wi-Fi?
Q4: Will 4G disappear?
Q5: When did 5G launch?
Conclusion
5G wireless technology is not simply the next step after 4G—it’s the foundation of our digital future. From driverless cars and smart grids to telemedicine and immersive education, this network is reshaping how societies function and how people interact with technology.
As adoption grows, the next decade will be defined by applications we can barely imagine today. If 4G connected people, 5G connects everything—ushering in a smarter, faster, and more connected world.










